Completed research projects
Research at 1:1 Scale
Numerous research projects with research and industrial partners require a research centre of this scale. The following projects provide a brief insight into our activities.
Dragon
2012 - 2015
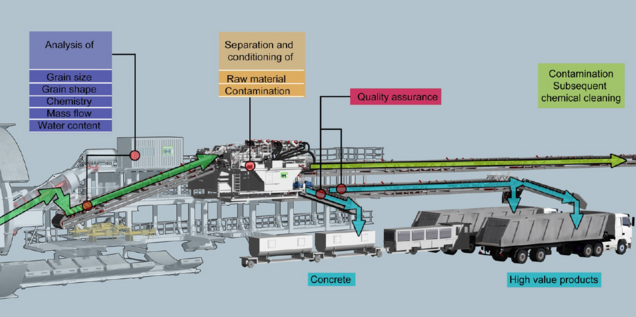
In the near future, the European civil engineering industry is expected to excavate around 800 million tons of mineral resources from tunnels, subway railroads and other underground structures such as underground power plants, sewage tunnels, etc. This material is usually disposed of in landfills. Currently, this excavated material is usually disposed of in landfills. Efficient use on site or in other industrial sectors is therefore of great economic and ecological interest.
RICAS2020
2015 - 2018
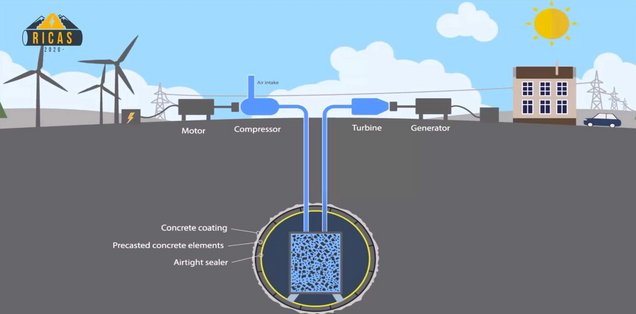
The RICAS2020 design study for the European underground research infrastructure related to advanced adiabatic compressed air energy storage (AA-CAES) will provide concepts for the development of a research infrastructure for the underground storage of very large amounts of green energy. The great advantage of the new concepts is that underground energy storage can be carried out regardless of the geological conditions and also in all locations with high energy demand. RICAS2020 is being built as an extension of the Research @ ZaB research infrastructure in Eisenerz, Austria, which is funded by the Austrian government and is designed as a European underground research, training and testing facility for underground mobility, including tunnels and subway railroads.
ETU-ZAB - Development of education and training standards for operations in tunnels and underground infrastructures
2018 - 2021
Austria has a large number of underground infrastructures, including road and rail tunnels, subway stations, energy supply systems, water supply systems, communication infrastructures and mining facilities. Due to fire disasters, terrorist attacks and mining accidents, safety in these structures has been increased. The consortium has set itself the goal of increasing safety in underground structures during the construction and operational phases and improving skills for dealing with emergencies in such infrastructures.
GEMEG - Geophysical-geomechanical rock mass classification for conventional and mechanized tunnelling
2018 - 2021
The FFG Bridge project aims to develop new geophysical measurement methods and mathematical solutions to overcome previously unknown geotechnical challenges in tunnel construction. The aim is to improve occupational safety and make the implementation of international tunnel construction projects economically feasible.
RecyMin - Recycling of artificial mineral fibers
2018 - 2022
Large quantities of mineral wool waste are produced during the demolition or conversion of buildings. Recycling this waste is currently not feasible in Austria, so mineral wool waste has to be landfilled. The aim of the project is to recycle and reuse mineral wool waste in the future. As a result, the project will create the basis for improving landfill properties through targeted processing steps, using mineral wool waste as a substitute raw material or grinding material in the cement industry, using mineral wool waste as backfill products and creating a concept for returning it to the mineral wool industry.
BRAFA
2019 - 2021
Vehicles with alternative fuels and drive systems will be increasingly used for climate and environmental reasons. However, the behavior of such vehicles in accidents involving fires is still largely unexplored. This research project aims to significantly improve the level of knowledge about the development, consequences and risks of fires involving vehicles with alternative drive systems.
Nike Bluetrack - Sustainable interdisciplinarity for complex underground operations
2020 - 2022
Complex underground operations are characterized by a lack of lighting and ventilation, the environmental conditions in a widely ramified infrastructure as well as a hybrid, proactive opponent and quickly push the emergency services to their limits as the depth of penetration increases. In such a scenario, orientation underground is of essential importance. Due to the multidimensional branching of underground structures, as well as the limited visibility and the resulting difficulties in orientation, the precise positioning of one's own forces is essential for survival.
ROBO-MOLE - ROBOtics for 3D mapping, orientation and localization in underground scenarios
2020 - 2022
The aim of ROBO-MOLE is to increase the safety of emergency services and civilians in tunnels and underground structures by detecting and identifying hazardous substances and automatically creating situation maps. A semi-autonomous robot with various sensors is being developed to take on supporting analysis tasks in operations such as hazardous goods transportation accidents in tunnels. The robot should be able to navigate and be controlled safely, even under difficult conditions such as smoke, heat or obstructed routes, in order to identify and map hazards.
DrainRepair - Adaptation of rehabilitation methods for drainage pipes in tunnel construction
2020 - 2023
The project deals with the maintenance and cleaning of drainage systems in tunnel structures to ensure their functionality. Particular attention is paid to the selection and optimization of rehabilitation methods for drainage pipes, with a focus on the CIPP method. Attention is paid to the fact that in some cases other methods may be more suitable. The aim is to reduce the cost of maintaining the tunnels and prevent damage to the drainage pipes.
BIM - Based planning, construction and operation process management in tunnel construction
2020 - 2023
The aim of this project is to ensure interoperability despite different company-internal designations so as not to impair internal company processes. To this end, a platform is being developed on which the company standards and their terminology can be translated into other standards. An industry standard can then be proposed from the sum of the various standards.
NIKE Submovecon - Sustainable interdisciplinarity for complex underground operations
2020 - 2023
The NIKE-SubMoveCon project aims to support security forces in dealing with terrorist threats in underground infrastructures. The sarin poison gas attack in Tokyo in 1995 highlighted the danger of such attacks in train, car and subway tunnels. A multidisciplinary approach, which includes automated multi-sensor analyses, assistance systems and individual and group sociology, is intended to produce key research results for operational strategies against terrorists in the field. This approach should enable the real-time generation of an overall situation picture in order to optimize the operational command of police, COBRA, the armed forces, rescue services and fire departments and thus significantly increase the safety of both civilians and emergency services.
FCCIS - Future Circular Collider Innovation Study
2020 - 2024
The Future Circular Collider Innovation Study is developing a conceptual design and implementation plan for a new CERN research infrastructure consisting of a 100 km ring tunnel and multiple surface sites. The project aims to attract academic and industrial leaders to develop a feasible and affordable plan that takes into account eco-design and resource efficiency. It involves collaboration with the host countries France and Switzerland to adapt the infrastructure to territorial constraints. CSIL is leading the project's financial planning team, which includes cost estimates, financing plans and socio-economic impact analysis. The socio-economic impact analysis will demonstrate the added value of the infrastructure in the first phase and serve as a basis for the development of a funding and implementation plan. The project emphasizes building user capacity with theoretical and experimental physicists at the international level to ensure the use of the facility from the outset. The FCCIS is organizing the international competition “Mining the Future”, which deals with the challenge of converting the important mining material molasse into a resource.
GeoDrone - Automatic geological AI interpretation of 3D images from outcrops taken with a drone
2021 - 2022
The aim of the project is the development, selection and application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms and the new development of AI architectures for the delineation of geological facies areas from 3D drone photos. In addition, the algorithm will be used to automatically interpret and estimate petrophysical properties and geomechanical properties. In order to achieve these goals, outcrops at the Zentrum am Berg (ZaB) in Eisenerz (Styria) are recorded using a drone. In addition, geophysical and geomechanical measurements are carried out selectively on these outcrops. With this data and the developed AI workflow, an automatic interpretation should now be possible. This will work faster and more accurately as the training input increases.
DrainML - Automation and machine learning for tunnel drainage diagnostics
2021 - 2023
As part of DrainML, a new machine learning-based solution for the diagnostics of tunnel drainage pipes is being developed. In addition to the existing automated cleaning of the drainage pipes, this should enable additional real-time diagnostics of these tunnel components.
NIKE DHQ-RADIV - Digital Head Quarters - Development of Rapid Data Integration and Visualization as a core process of staff work
2021 - 2023
Current and future operations are very complex, so a comprehensive situational picture is necessary to reduce complexity and provide decision-makers with the information they need. Especially in urban environments, large amounts of heterogeneous data need to be integrated and visualized. NIKE DHQ-RADIV is part of the overall NIKE program and aims to quickly integrate and visualize data to create a comprehensive operational picture. It is designed to ensure the collaboration of different visualization systems across the reality-virtuality continuum. Currently, there are only individual applications without collaboration options.
NIKE-MED - Sustainable interdisciplinarity in complex underground operations - Medical Treatment
2021 - 2023
Complex underground operations are associated with a large number of typical injury patterns that represent a major challenge for the healthcare system. These include poisoning from combustion gases, extensive burns, gunshot and fragmentation injuries, mental disorders, contamination with NBC substances and injuries caused by mass panic. NIKE MED evaluates emergency capacities, develops an application to optimize care for emergency services and identifies the need for strategic reserve capacities. The project makes an important contribution to the operational readiness of specialized underground task forces and to national crisis and disaster management.
MED1stMR - Training medical first aiders with a mixed reality approach
2021 - 2024
The MED1stMR research project aims to better prepare medical first responders for stressful and highly complex disaster situations. Using a mixed reality training system, medical action routines can be practiced realistically in order to improve reaction speed and coping strategies. Thanks to wearable technology for monitoring the physiological data of the trainees, training is to be supported and personalized. Smart electronic devices in the project can detect and transmit biosignals to provide debriefing and control adaptive smart scenarios based on artificial intelligence during training.
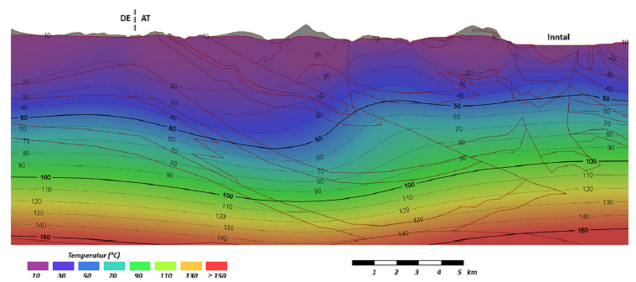
A pre-feasibility study on deep geothermal energy in Tyrol
2022 - 2023
The aim of the project is an initial assessment of the potential for the possible use of partial geothermal energy in the Inn Valley. An interdisciplinary team (geologists, geophysicists, earthquake researchers and geotechnical engineers) is carrying out an extensive initial data collection.
More about the study can be found here: link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00501-023-01405-9
IGNITE: Improved assessment of the risk of forest fires in Austria
2022 - 2024
The IGNITE project aims to improve the FWI for the whole of Austria and optimize the assessment of the risk of forest fires. The basis for this are i) in-situ measurements in different forest types, ii) ignition experiments at the Centre on the Mountain of the University of Leoben, iii) the creation of a spatially high-resolution vegetation index for the risk of forest fires, taking into account tree species, gaps, litter moisture and topography, and iv) the validation/reparameterization of the FWI using existing forest fire data, the empirical data obtained and causal machine learning approaches.
EVUB
2022 - 2024
The aim of this project is to define the relevant geo-factors, infrastructure and movement areas and to establish the basis for a three-dimensional representation in a data structure that can be used by the Austrian Armed Forces. For this purpose, a prototype is to be created for a small area with real data, which allows the vivid representation of a complex spatial structure and goes significantly beyond the possibilities of conventional elevations and floor plans. To create the prototype, it is necessary to develop new survey methods and survey technologies.
In2Track3
2023 - 2023
In this project, a UGV (unmanned ground vehicle), also known as a Tunnel Drainage Rover (TDR), was developed. This UGV can work under different conditions in tunnel drainage systems (different pipe diameters and geometries, humidity). With an embedded camera sensor, it detects obstacles remotely. The UGV was used under real conditions in the drainage system at Zab.
Faserbetontübbingen
2023 - 2024
At the segment test stand of the Chair of Subsurface Engineering at the University of Leoben, segments are tested on a scale of 1:1 for compliance with specified load-bearing capacity criteria. In the current research project “Fiber-reinforced concrete segments”, segments with pure steel or plastic fiber reinforcement are being tested and compared with conventional steel bar reinforcement. In cooperation with scientific and industrial partners, the aim is to create a basis for the use of fiber-reinforced concrete segments in Austria.
AI-4Geothermal
2023 - 2024
The AI4Geothermal project aims to use AI algorithms to improve the interpretation of geological structures from laser scan data. Models are developed and tested using PyTorch and TensorFlow in a Google Colab environment. The project aims to create an efficient workflow for geological surveys, including underground and aerial applications. Expected benefits include faster and more accurate assessments of geothermal reservoirs, reducing costs and supporting environmental sustainability. The collaboration with Montanuniversität Leoben ensures that advanced AI techniques are integrated into geophysical studies.
STUVA analysis of reaction and escape behavior
2023 - 2024
Several serious fire accidents in the Alpine countries in 1999 and 2001 were one of the triggers for improving safety in road tunnels. In the BAST booklet B66 “Safety assessment of road tunnels”, a quantitative methodology for the safety assessment of road tunnels was developed. In order to increase the data basis, initial investigations are being carried out on the basis of several large group tests (at least 6 people per group) and real tests on the test setting or scenario “vehicle collision with fire development” using a resilient sample that represents the breadth of society. “The aim of the project is to develop in-depth findings on group effects in the self-rescue of tunnel users as well as derived escape and reaction times.”
Solarfold pull-out tests ground anchor
2024 - 2024
The company solarfold GmbH manufactures mobile solar containers for flexible power generation. The almost 130 m long photovoltaic systems are set up semi-automatically from the containers using an aluminum rail system. This rail system rests on supports which are fixed to the ground with polygon anchors. Three ground anchor bolts are used as foundation elements for each polygon anchor.
The aim of the project is to determine the maximum pull-out forces of the ground anchor bolts in field tests for different soil types (soft, medium-hard and hard), which are to be regarded as representative soil types for Slovenia, Germany and Austria. Pull-out tests for four different soil types were carried out at the Zentrum am Berg (ZaB) in Eisenerz using the manually displaced ground anchor bolts.