Actual Research Projects
Research at 1:1 Scale
Numerous research projects with research and industrial partners require a research centre of this scale. The following projects provide a brief insight into our activities.
TransIT
2020 - 2025
In the TransIT project (platform for digital transformation in civil engineering and tunnel construction), research groups from the University of Leoben, the Johannes Kepler University Linz and the Vienna University of Technology are working on the implementation of digitalization topics in civil engineering and tunnel construction in a multidisciplinary manner with complementary expertise.
More on this at: https://www.tunnellinghub.at/!
ET-PP - Einstein Telescope Preparatory Phase
2022 - 2026
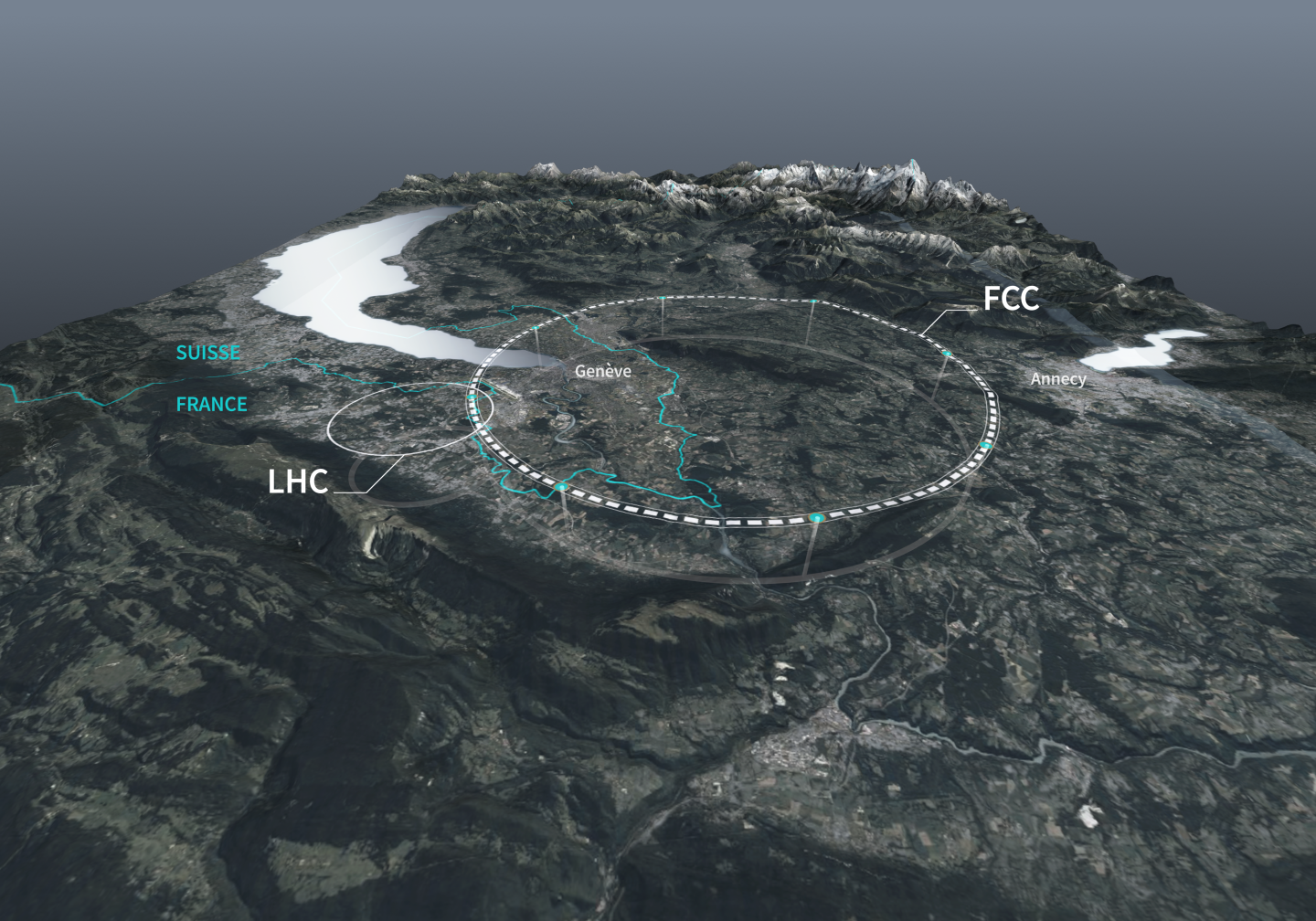
The underground Einstein telescope will take research into gravitational waves and black holes to a new level across Europe. The telescope will consist of 3 tunnels of 10 km each, the ends of which will lead into caverns for the detection of gravitational waves. Sardinia and the Euregio Meuse-Rhine in the border region of Belgium, Germany and the Netherlands are considered to be optimal locations, which must be free of background noise. As with every major project, sustainability is a top priority right from the planning stage. In addition to site preparation, technical design and calculation and data models, work is also being carried out on a solution for the use of the resulting 5 million m3 of excavated material in order to keep the carbon footprint of the Einstein Telescope as low as possible.
Pühiko Nukutü: A green hydrogen geostorage battery in Taranaki
2022 - 2027
The aim of this exploration is the technical implementation and cost efficiency of larger storage volumes of hydrogen. As well as the socio-ecological effects of hydrogen volumes in excess of 50,000,000 Nm³ in sedimentary rock.
LUQUAS
2023 - 2025
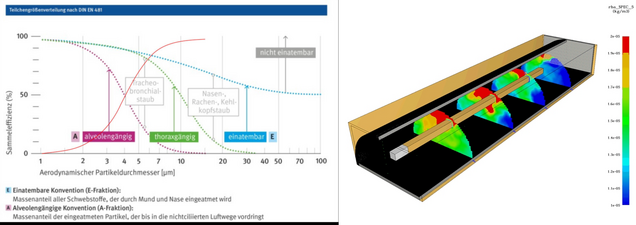
The project aims to reduce hazardous substances in underground mining using blasting technology and diesel generators. This is to be achieved through practical technical measures in order to comply with legal limits and prevent occupational illnesses. To this end, pollutants are measured online and correlated with laboratory measurement data.
NIKE-Swarm Nav - Robot navigation without GNSS signal, UAS/UGV swarms, autonomous systems
2023 - 2025
The project pursues situational awareness in complex urban environments as the scene of military conflicts, in such situations systems of unmanned ground platforms (UGV) and drones (UAS) - as “agents” - can be used in a swarm network for reconnaissance. The project in question, NIKE-SwarmNav, aims to develop components that enable a swarm of UGVs and UAS to navigate and operate in areas without a GNSS signal. Particularly innovative here is the interaction of the on-board sensor combination for navigation (LIDAR, UWB, camera, inertial sensors), from whose fused data the states are estimated independently of a GNSS signal. The combination with swarm coordination methods enables cooperative state estimation. In the end, these components are subjected to a functional verification in realistic laboratory environments at the Zentrum am Berg on specially developed carrier platforms consisting of UGV and UAS.”
AI-Q Ready
2023 - 2026
A-IQ Ready explores cutting-edge quantum sensor technology, the use of AI in edge environments and distributed collaborative technologies. Quantum magnetic flux and gyro sensors enable the highest sensitivity and accuracy without the need for calibration and provide unmatched performance when deployed in a non-GPS enabled environment. Such a localization system will improve the timing and accuracy of autonomous agents and reduce false alarms or misinformation through AI and multi-agent system concepts.
Archimedes
2023 - 2026
Archimedes develops components, models and methods to increase the efficiency and service life of drive components, power components and energy storage systems in the automotive, aviation, infrastructure and industrial sectors. This supports the energy transition on the consumer side. To support this mission, ARCHIMEDES aims to transform technologies and products in automotive, aviation, infrastructure safety and the related ecosystem towards a resilient, decarbonized, digitalized and green EU.
I-WASP
2023 - 2026
The I-WASP project is therefore dedicated to the question of how the complex processes on a tunnel construction site after the NATM can be automatically recorded, analyzed and optimized using innovative methods of data acquisition, transmission and processing - including methods of artificial intelligence (AI).
DuAList
2024 - 2025
DuaList aims at the focused further development of the LED approach as a sensor in traffic infrastructure with two planned use cases, the monitoring of traffic and the detection of environmental and weather conditions. In the following, these two cases are abbreviated as the monitoring use case and the weather use case. The dual use of LEDs enables a compact design. This supports the objective in both applications of implementing a retrofitting solution for existing lighting in the traffic infrastructure, i.e. only the light sources and their peripherals need to be replaced, without the need to replace the housing, cabling or mechanical fixings.
CHEMATUN
2024 - 2025
Underground infrastructures are of crucial importance for modern transportation concepts, especially in Austria. While tunnel safety has largely focused on fire incidents, the release of hazardous substances in tunnels has been little researched. The unique characteristics of tunnels, including ventilation systems and drainage, significantly affect the dispersion of chemical agents and make response strategies complex. Research to date has mainly focused on tunnel fires, leaving gaps in knowledge regarding the behavior of hazardous materials and the effects of ventilation.
The CHEMATUN project aims to develop response strategies for chemicals in tunnels by studying their dispersion under real conditions in the center on the mountain. Through large-scale gas release experiments, the project will provide important data for emergency planning, ventilation strategies and the development of protective equipment.
Heatrock
2024 - 2027
Large heat storage facilities are indispensable for the efficient use of climate-neutral waste heat and energy and for the expansion of district heating networks. In Austria, there are many potential locations for cavern storage facilities near city centers. Cavern storage facilities have a very long service life and are barely visible. The main objectives of the “HEATROCK” project are to further develop the technology “optimized cavern storage for seasonal balancing in urban district heating networks” and to reduce the specific investment costs of cavern storage.
NNATT
2024 - 2026
In contrast to the HORIZON 2020 project DRAGON, which was completed in 2015, the NNATT project is designing a holistic system for the sustainable use of excavated materials from civil engineering and tunnel construction, which, in contrast to the current state of the art, starts with mineralogical, petrographic and geochemical as well as geotechnical parameters and extends through construction logistics and construction process engineering to industrial application. The basis is a decision matrix based on artificial intelligence (AI), which is used to separate excavated materials in real time based on mineralogical, petrographic, geochemical and geotechnical information from the preliminary exploration of a civil engineering or tunnel construction project, in combination with AI-supported and sensor-based analyses.
CERN Open Sky Lab
2024 - 2027
The FCC Innovation Study requires evidence of a credible scenario for the prevention, reduction and compensation of landfilling of excavated material. During the “Mining the Future” competition, a potential reuse process based on the pre-treatment of excavated material and incubation with fungi, bacteria and microorganisms to produce fertile soil for a wide range of applications in renaturation, agriculture and forestry was identified. Depending on the type of soil organisms added, the aim is to use the product in various ecosystems without jeopardizing biodiversity.